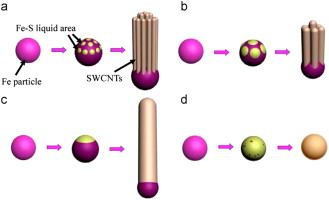
ABSTRACT: Understanding the growth mechanism of carbon nanotube is important to control the structure and properties of carbon nanotubes. We examined several aspects of the single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) prepared by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes using ethanol with the additions of ferrocene and thiophene, focusing on the potential mechanisms leading to the differences in the diameters, structures, and conductivities of the SWCNTs formed. The diameter of SWCNTs could be controlled from ∼1.0 to ∼5.8
nm by adjusting the concentration of thiophene used. The larger diameter SWCNTs has a higher thermal stability than smaller-diameter SWCNTs. With increasing diameter, the electrical properties of the SWCNT change from mainly semi-conducting to metallic-like. The growth mechanism of SWCNTs was subsequently studied to understand the mechanism of thiophene controlled SWCNTs formation. This study could lead to improved control over the diameter and electronic properties of SWCNTs.