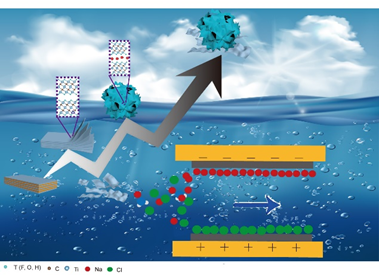
Abstract: MXene has been known as an important candidate material in the field of electrochemical energy storage. Different etching methods have an important effect on the properties of MXene. Herein, we prepared Ti3C2Tx MXene by LiF/HCL-etching method and applied it firstly in capacitive deionization. The method of LiF/HCletching is beneficial to increase the interlayer spacing of Ti3C2Tx and reduce the content of –F in termination groups which are favourable for ion transport. An ultrahigh desalination capacity of 68 mg·g-1 is achieved at a current density of 20 mA·g-1 and a voltage window of 1.2 V. Furthermore, the relatively low energy consumption of 0.24 kWh/kg-NaCl is achieved, and the energy recovery is 5.44%. The LiF/HCl-etched Ti3C2Tx displays a promising ability for desalination in capacitive deionization, making Ti3C2Tx be a promising candidate
for CDI electrode materials.
Keywords:Ti3C2Tx; MXene; LiF/HCL-etching; Capacitive deionization; Desalination