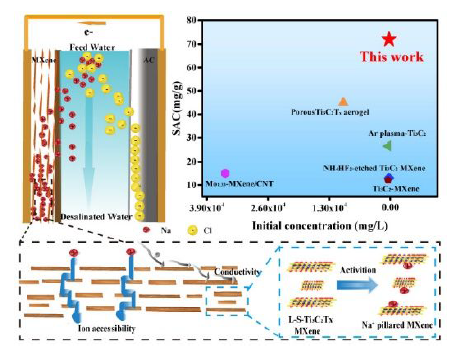
Abstract: 2D-Ti3C2Tx MXene flake restacking and the small interlayer spacing of these MXenes limit their application in capacitive deionization. Here, we designed an all-MXene-based (L-S-Ti3C2Tx) flexible film electrode, enabled by large-size Ti3C2Tx (lateral dimensions of ≥ 1 μm) MXene (L-Ti3C2Tx) nanosheets, which provided conductive pathways and were active substances, and by small-sizeTi3C2Tx (500 nm) MXene (S-Ti3C2Tx) nanosheets, which were used as intercalation materials and active substances, for high performance desalination in capacitive deionization applications. The as-synthesized L-S-Ti3C2Tx electrode achieved an excellent capacitance (169 F/g at 5 mV/s) and long-term cycling stability (maintained 91.7% of the initial capacitance after 5000 cycles). Additionally, these electrodes exhibited a high electroadsorption capacity (72 mg NaCl/g L-S-Ti3C2Tx, 10 mM NaCl solution). The improved electrochemical and desalination performance and outstanding long-term cycling stability can be attributed to the small Ti3C2Tx sheets that were introduced, which could be beneficial in exposing more active sites, facilitating electron transport and shortening the diffusion path of Na ions. Our work opens up a new design space for the development of high performance anode materials
Keywords: Capacitive deionization; Ti3C2Tx; MXene; Intercalating agent; Desalination