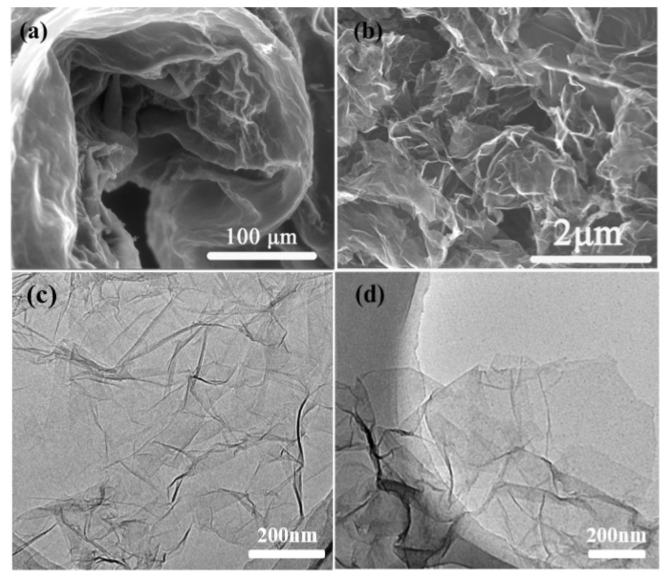
ABSTRACT: An efficient and environmentally friendly synthesis method was applied for preparation of graphene hydrogel (GH) adsorbents via one-step hydrothermal reduction. By means of characterizations, the possible assembly mechanism of GH was discussed. The Response surface methodology (RSM) was firstly used to evaluate systematically the interactions of synthesis reduction conditions (i.e. graphene oxide initial concentration, reducer dosage, temperature and reaction time) on GH adsorption capacity of CIP. The affecting degree order of the four factors on the adsorption capacity was obtained, thus provide a guidance for GH adsorbents design. In addition, the adsorption enhancement effect of water in GH was raised. Besides, the multiple ciprofloxacin adsorption mechanisms of GH were also investigated and summarized, indicating GH possesses a promising potential in practical application. This finding indicates that GH may be an efficient adsorbent for antibiotic pollutants removal in water purification.