ABSTRACT: Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) were fabricated and oxidized by different concentrations of sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) solutions. The untreated MWCNTs and modified MWCNTs were employed as adsorbents to study their characterizations and adsorption performance of toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene isomers (TEX) in an aqueous solution. The physicochemical properties of MWCNTs were greatly affected after oxidation, which influences TEX adsorption capacity. The 3% NaOCl-oxidized MWCNTs shows the greatest enhancement in TEX adsorption, followed by the 30% NaOCl. More interestingly, the 15% NaOCl-oxidized MWCNTs has lower adsorption capacities than untreated MWCNTs. The adsorption mechanism of TEX on treated MWCNTs is attributed to the combined action of hydrophobic interaction, π-π bonding interaction between the aromatic ring of TEX and the oxygen-containing functional groups of MWCNTs and electrostatic interaction. 3% NaOCl solution could not only introduce much oxygen-containing functional groups on MWCNTs, but also lead to less damage for the pore structure. This suggests that the CNTs-3% NaOCl is efficient adsorbent for TEX and that they may possess good potential for TEX removal in wastewater treatment.
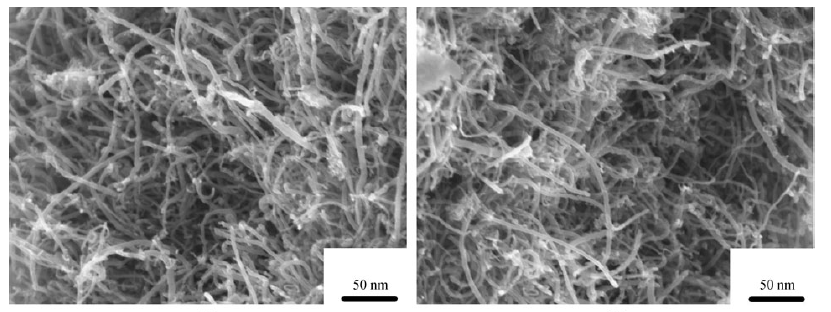
.