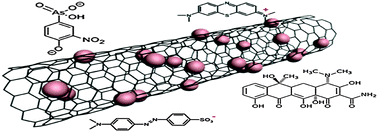
ABSTRACT: The adsorption of organic pollutants, including dyes (methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO)), antibiotics (tetracycline (TC)), and organic arsenical compound (roxarsone (ROX)), has been studied on a new kind of CNT/C@Fe/CS nanocomposite. The effect of solution pH, contact time, and temperature on adsorption properties has been studied. The adsorption process follows the pseudo-second-order kinetic model very well, and equilibrium studies fit well with Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin adsorption isotherms. The maximum uptakes of MB, MO, TC and ROX on CNT/C@Fe/CS are found to be 111.1, 500.0, 125.0, and 142.9 mg g1, respectively. Parameters calculated from thermodynamic indicate that the adsorption process is exothermic, spontaneous and favorable. The removal of organic pollutants is obviously dependent on pH values and temperature. These results suggest that the CNT/C@Fe/CS nanocomposite could be effectively used for the removal of organic contaminants from wastewaters.